Briefly Explain the Difference Between Primary and Secondary Deviance
If the deviant feels theres nothing he can do to change societys perception of him he will continue to commit deviant acts. Primary sources can be described as those sources that are closest to the origin of the information.
Primary Secondary Deviance Rectoria Unal Edu Co
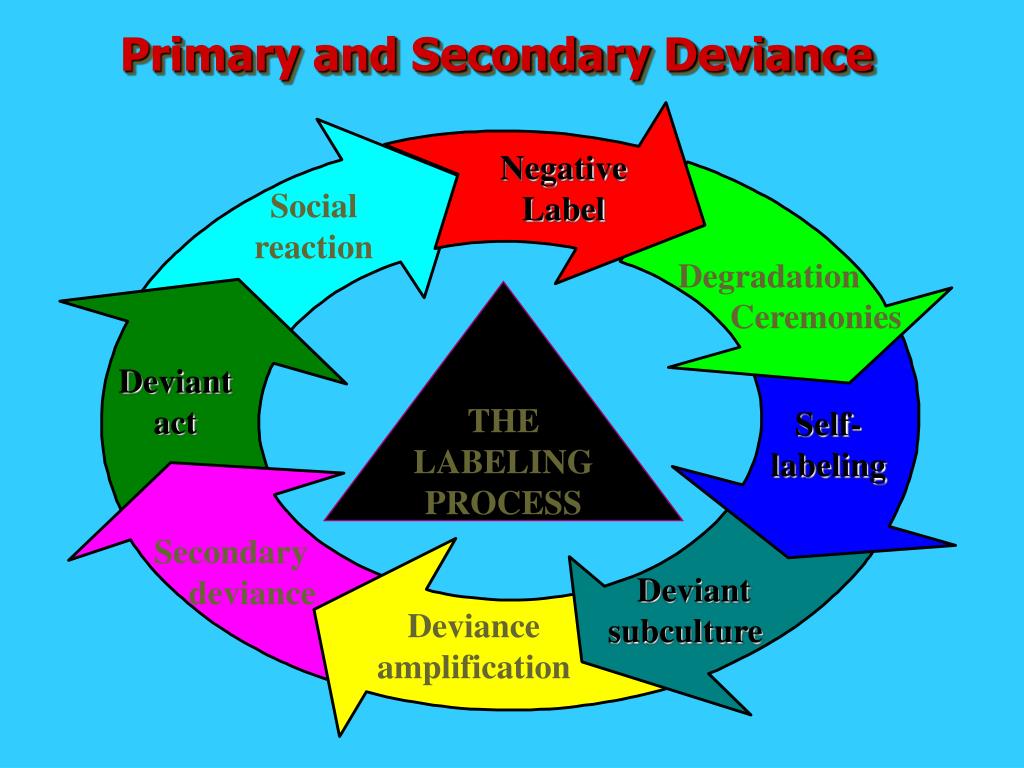
The idea of primary and secondary deviance comes from the interactionist Lemert.

. Thus a positive self-image can be maintained which goes hand in hand with ones own role in society. However in secondary deviance the person is already labeled as a deviant but still hshe continues to engage in that particular act. Secondary deviance then occurs when this same teenager moves to a different school and smokes in.
Reaction is not particularly negative or stigmatizing. Suggesting that there was a primary and secondary stage of deviancePrimary deviances are acts which havent been publicly defined as deviant due to the fact that theyre minor and insignificant incidents of rule-breaking. It was Edwin Lemert who introduced primary and secondary deviance as a part of his labeling theory.
Labelling theory and deviance 2. Activities that cause harm not necessarily only those that break current. These sources are documents that relate to information that originated elsewhere.
Difference between primary and secondary deviance. Concepts of health wellbeing and illness and the aetiology of illness. Deviance is behavior that is recognized as violating expected rules and.
3 Briefly explain the difference between primary and secondary deviance. An example of primary deviance would be skipping school. Primary deviance is basic violation and secondary deviance is when they integrate it in to self-concept.
4 Define self-fulfilling prophecy. What are the principles of restorative justice. This includes getting to know of ones society and culture.
What it is to do gender Provide an overview of feminist perspectives in criminology. The primary deviance is of little consequence. Explain the differences between consensus and conflict perspectives in sociology.
Secondary deviance occurs if the label from primary deviance sticks. Green crime refers to crimes committed against the environment. They contain raw information and thus must be interpreted by researchers.
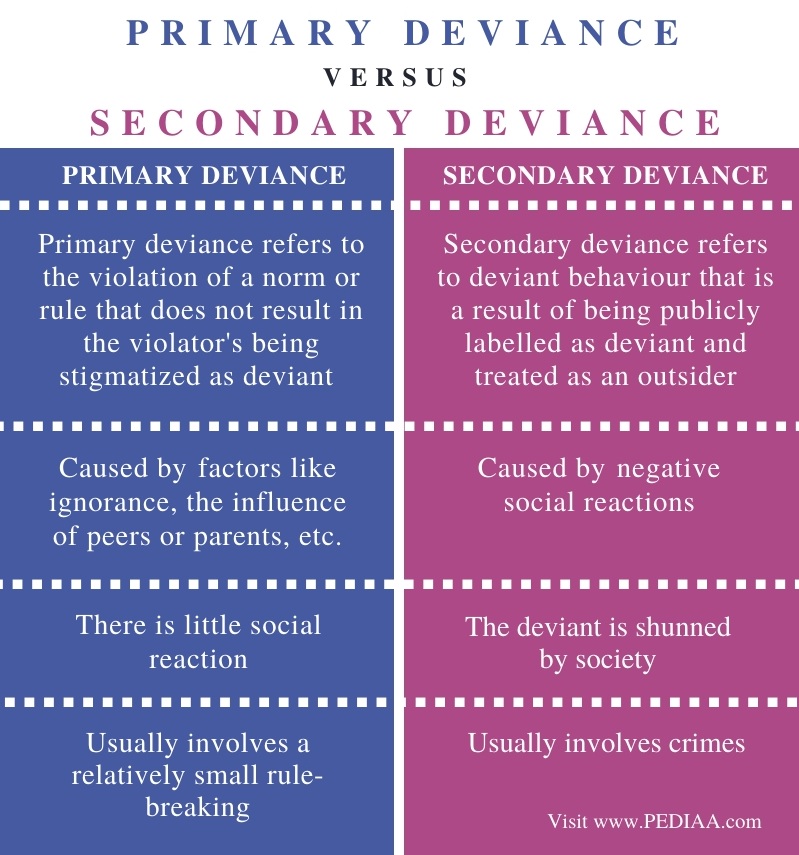
10 Suggest one criticism of. While primary deviance is recognized as undesirable it has no further effect on the status and self-image of the deviants. Difference Between Primary and Secondary Deviance Definition.
62 Socialization is the development of culture within a person teaching him or her values norms and roles. The difference between primary deviance and secondary deviance is in how the deviant self-identifies after society labels his actions as deviations from the norm. The taking on a deviant identity by talking acting or dressing in a different way rejecting the people who are critical and repeatedly breaking the rules.
The Relations Between Socialization Crime and DevianceNicolas WeidlStudent ID. Therefore the Option A is correct. Let us first gain a general idea of socialization before looking at the difference between Primary and Secondary Socialization.
Primary deviance is the first event that is punished. Their deviance is a result of their socialization. The same adolescent moves to a new school where his peers never smoke and where smoking is considered a deviant behavior.
Differentiate between primary deviance and secondary deviance. Primary deviance does not lead to a permanent label from external observers or to a deviant self-identity on the part of the offender. It is through this that the child learns the attitudes.
May result in primary deviance while. An example of secondary deviance would be bitter towards those who dont agree and repeatedly keep skipping school. Secondary deviance- any type of deviant behavior in which the.
This is secondary deviance. This also creates self-awareness as individuals interact with others Brym Lie Rytina 2010100 for this reason. Primary deviance- any type of initial deviant behavior in which the perpetrator does not identify with deviance.
5 Suggest two advantages of labelling theory. Socialization refers to the process whereby an individual mostly a child becomes socialized. For instance a teenager who smokes cigarettes with other teens doesnt perceive any bad behavior because everyone else in the peer group is smoking.
The investigation of green crime is the focus of green criminologists. The primary deviance is considered to be the initial manifestation of deviance The secondary deviance is considered to be the effect of primary deviance. The students call him names and exclude.
6 Give two criticisms of labelling theory. Whilst secondary deviance are acts which have been publicly listed and labeled as deviant. -Primary deviance refers to the violation of a norm or rule that does not result in the violators being stigmatized as deviant but secondary deviance refers to a deviant behavior that is a result of being publicly labelled as deviant and treated as an outsider.
8 Define moral panic. Moreover factors like ignorance the influence of peers or parents etc. However the societal reaction to that action could lead to secondary deviance.
Secondary sources are closely related to primary sources and often interpret them. 7 Briefly explain a deviancy amplification spiral. Primary deviance refers to the violation of a norm or rule that does not result in the violators being.
Secondary deviance is not simply a violation of social norms but a violation. Primary and secondary deviance 1. Deviance is behavior that violates norms and rules of society and crime is a type of deviant behavior that violates the formal criminal law.
An example would be first time violations of the law are primary deviations. If one acts in an isolated deviant way this is primary deviance. 9 Define folk devils.
Hence the difference between the primary and secondary deviance is that the Secondary deviance is an eventual effect of primary deviance where deviance begins. We are currently in the process of updating this chapter and we appreciate your patience whilst this is being completed. In primary deviance the person commits a deviant action without knowing that hshe is going against the norm system.
How do sociologists conceptualize and explain deviance and crime. Primary deviance usually occurs within a persons own peer group that engages in the same behavior. Criminology is the study of crime from a scientific perspective.
Concepts of primary and secondary deviance This section covers. Critics said Miller exaggerated the differences between the value systems in poor inner-city neighborhoods and wealthier middle-class communities Akers Sellers 2008. The deviant does not define himself by deviance but rationalizes and trivializes it.
If boys grow up in a subculture with these values they are more likely to break the law. Primary deviance is the act itself. Green criminologists are transgressive criminologists in that not all the activities they are interested in would necessarily be of interest to traditional criminology.
In other words if that person is then labelled as deviant and internalises that label then. Secondary deviance includes repeated deviant behavior that is brought on by other peoples negative reactions to the original act of primary deviance.
What Is The Difference Between Primary And Secondary Deviance Pediaa Com

0 Response to "Briefly Explain the Difference Between Primary and Secondary Deviance"
Post a Comment